
Business operators must weigh out the economic value to the company, including the book value, residual value, and the useful life of the intangible asset. An example of amortization would be the allocation of $100,000 in patent expenditure over a useful life of 10 years. Under the straight-line method, the annual amortization expense is $10,000, reducing the book value of the patent during this time, thereby capturing its reduced economic benefit. In a lending context, which you may also encounter as an investor in real estate investment trusts or mortgage-based investments, amortization is a technique by which loan financing is configured. Like amortization for accounting, the value of an asset decreases over time, but in this case, it’s a loan. The sum-of-the-years digits method is an example of depreciation in which a tangible asset like a vehicle undergoes an accelerated method of depreciation.
Business Advisory and Consulting: Make Your Company Better
As a non-cash operating expense, amortization decreases reported earnings, while not impacting the company’s cash flow. It automates the feedback loop for improved anomaly detection and reduction of false positives over time. We empower accounting teams to work more efficiently, accurately, and collaboratively, enabling them to add greater value to their organizations’ accounting processes. Typically uses the straight-line method, spreading costs evenly over the asset’s useful life. To systematically allocate the cost of an intangible asset over its useful life. The dollar amount represents the cumulative total amount of depreciation, depletion, and amortization (DD&A) from the time the assets were acquired.
- This accounting function allows the company to use and capitalize on the patent while paying off its life value over time.
- Key features of this method include higher initial payments, which decrease over time, and a larger initial impact on the balance of the loan or asset.
- Though the notes may contain the payment history, a company only needs to record its currently level of debt as opposed to the historical value less a contra asset.
- Amortisation is neither good nor bad, but there are certain benefits and downsides to its utilisation.
- There are easy-to-use amortisation calculators that can help you figure out the best loan principal repayments schedule, taking into account the interest rates and loan type and terms.
- Instead, it represents the allocation of a cost already incurred (when the intangible asset was acquired).
Periodic review and adjustments
- You should record $1,000 each year in your books as an amortization expense.
- A loan is amortized by determining the monthly payment due over the term of the loan.
- Estimate the number of years the asset will contribute to generating revenue for the business.
- It is what is accounted for on the income statement and it represents the cost of tangible assets allocated to the accounting period.
- Amortizing lets you write off the cost of an item over the duration of the asset’s estimated useful life.
- An example of an amortized intangible asset could be the licensing for machinery or a patent for your business.
A higher percentage of the flat monthly payment goes toward interest early in the loan, but with each subsequent payment, a greater percentage of it goes toward the loan’s principal. While amortization applies to intangible assets and specific financial instruments, depreciation is used for tangible assets like buildings or machinery. For businesses, amortization is crucial in determining the true value of intangible assets over time. This is important for investment analysis, business valuations, and when considering mergers or acquisitions.
Loan modifications
This knowledge empowers them to make informed decisions regarding investments and resource allocation. If a borrower refinances the loan, makes extra payments, or misses payments, the original amortization schedule is modified. Extra payments reduce the principal faster, potentially shortening the loan term and reducing the total interest paid. In certain cases, particularly for small and low-value intangible assets, companies might choose to expense the entire cost in the year of purchase. In some cases, an intangible asset might have a residual value at the end of its useful life, although this is less common than with tangible assets.

What is an example of amortisation?
Fixed Assets are long-term assets used in the operation of a business, such as buildings, machinery, and equipment. Also, considering that the use of certain assets might have social or environmental implications, the application of amortization can help represent these costs fairly. This, in turn, can effectively contribute towards CSR initiatives, supporting companies’ commitment towards environmental stewardship, fair labor practices, or other socially responsible activities.
To account for this premium, periodic interest adjustments are made to gradually reduce the discount over time. These adjustments involve allocating a amortization refers to the allocation of the cost of portion of each interest payment towards reducing the premium. As a result, the bond’s book value decreases, approaching its face value by maturity.
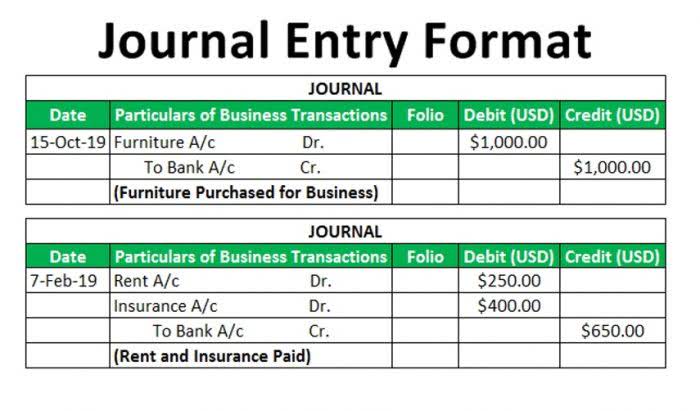

We amortize a loan because loans become a kind of financial liability and are not tangible assets. Amortization, therefore, refers to the systematic way of paying interest and principal over some time and reflects a decrease in the balance of a loan on the balance sheet. Depending on what you’re investing in, you may need to understand the declining value of intangible assets, or the way that many loans are structured. You must use depreciation to allocate the cost of tangible items over time. Likewise, you must use amortization to spread the cost of an intangible asset out in your books.
#2. Declining balance method
If a company is going to amortize something, it will have an attached amortization schedule. This schedule is a table detailing the periodic payments of said loan or asset. These regular installments are generated using an amortization calculator. The allocation of costs over a specified period must be paid in full by the time of the maturity date or deadline. If the patent runs for 30 years, the company must calculate the total value of the intangible to the company and spread its monthly payment over this asset’s life.
Depreciation
There are several steps to follow when calculating amortization for intangible assets. Since intangible assets are not easily liquidated, they usually cannot be used as collateral on a loan. Furthermore, amortization enables your business to possess more income and assets on the balance sheet. Revenue is the total income generated by a business from its normal business operations, usually from the sale of goods and services to customers. Profit, also known as net income, is what remains after all expenses, taxes, and costs have been subtracted from revenue. While revenue measures the total sales, profit measures the actual earnings after all financial obligations are met.
